

The most effective form of treating an ear hematoma is surgery. The doctor will inspect the ear canal, swab it for a sample and then examine the sample under a microscope for parasites or signs of an infection. This may involve the very tip of the ear or it may occlude the ear canal.Įar hematomas can be diagnosed during a physical exam. The swelling will sometimes seem firm and other times it will be soft and fluctuant.
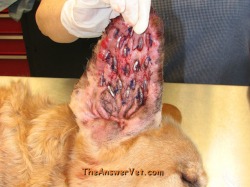
Pets that are suffering from ear hematomas will have fluid-filled swelling on either all or just part of their ear flap. Ear mites or yeast/bacterial infections are commons causes of a pet shaking their head and scratching. When this happens, the trauma causes blood to leave the vessels and pool in a pocket on the outer part of the ear flap, between the cartilage components and skin. This results in their ear flaps slapping against the skull. An example of this is when a pet fervently shakes their head or scratches at the ears.
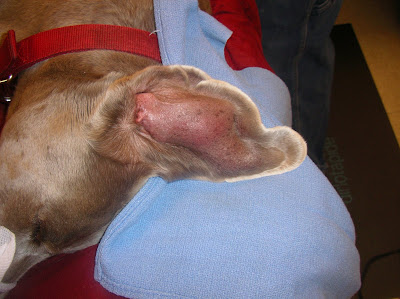
Self-trauma is a leading cause of ear hematomas.
#CANINE AURAL HEMATOMA SKIN#
Both cats and dogs can be afflicted with ear hematomas, however canines, especially those who get skin allergies and ear infections, are more prone to ear hematomas.Īny breed of dog or cat can develop an ear hematoma, and since allergic skin disease is a common cause, pets that are prone to skin allergies are very likely to develop an ear hematoma. This is usually caused by overly aggressive head shaking or ear scratching that results from an ear infection. An ear/aural hematoma is a pool of blood that collects between the cartilage and skin of the ear flap of a pet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
